Table of Contents
- What are rubble foundations and what features of stone structures?
- Methods of waterproofing rubble masonry and foundation
- Prices for waterproofing arrangement
Today there is a huge number of materials used for the construction of foundations of various structures. However, several decades ago, the technology of foundation construction was not so developed and diverse. At that time, it was customary to use natural stones for the foundation of the building, which are stacked on top of each other and fastened with the ground, clay, and other compounds. Foundations made using this technology are called rubble foundations.
Stone, like other materials, should necessarily be protected from the effects of water and moisture with materials capable of protecting buildings and living quarters from the effects of water. This article will be discussed the features which are characteristic of rubble foundations and rubble masonry, as well as what methods are used in modern construction to protect the stone from the harmful effects of water.
What are rubble foundations and what features of stone structures?
As practice shows, the stone base is universal and suitable for almost all types of structures. The rubble foundation serves as reliable support for buildings made of wood, brick, and concrete, as well as other light and heavy structures. Moreover, the ability of the stone to withstand loads directly depends on the depth of its laying.
Often, such a foundation becomes the basis for non-residential structures, such as baths, greenhouses, sheds, and the like. For such structures, the foundation can be installed on dense layers of soil, in the case of residential buildings, the rubble base is necessarily fixed below the ground freezing level.
Among the features of the type of foundation under consideration, a large number of positive properties can be distinguished, for example:
- Strength;
- Long service life;
- Frost resistance;
- Hydrophobic properties;
- Environmental safety.
The high strength of the stone foundation allows it to be installed without internal reinforcement, which is especially important for non-residential structures.
Among the disadvantages of a rubble foundation, the following points can be distinguished:
- The complexity of the construction of a stone foundation;
- High duration of foundation installation;
- The complexity of material transportation;
- Relatively high cost.
The last drawback does not always turn out to be true, since the cost of stone directly depends on the distance between the construction site and the quarry for stone extraction, as well as on the characteristics of the territory, including climatic ones. In different regions, the installation of a rubble foundation is a process of varying complexity.
For example, in a rocky area rich in necessary materials, work costs an order of magnitude cheaper than in areas characterized by plains. In this case, a significant part of the amount is allocated for the delivery of heavy stone from the mining site to the construction site.
The reliability of the rubble foundation directly depends on how correctly it was installed. At the stage of the construction of a stone foundation, factors such as the nature of the soil on the construction site, the properties of the butte, the planned type of foundation, the number of materials required for construction, and so on are necessarily taken into account.
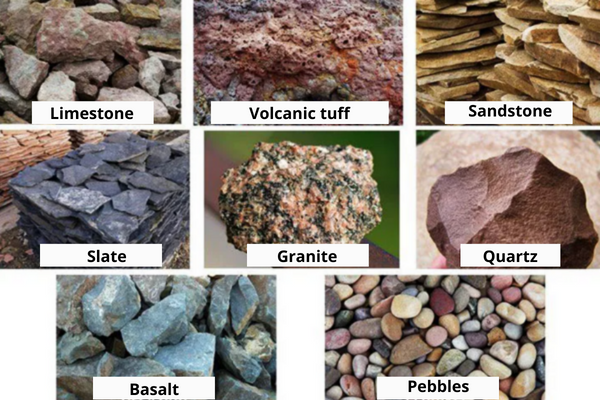
To date, flat stones or flagstones are considered the most convenient for foundation construction. This type of stone includes rocks characterized by a layered structure. During mining, rocks are split into slabs of different sizes and shapes, with approximately parallel faces. Due to this feature of the flagstone, the laying of the rubble foundation is carried out with minimal consumption of mortar.
Other buta rocks used for laying the foundation — are slate, dolomite, tuff, limestone, sandstone, and shell rock. Sometimes even such a difficult-to-use material as river cobblestone is used. The complexity of its installation is explained by its characteristic rounded shape, which, as a rule, is harder to work with. At the stage of choosing a booth, it is necessary to rely on the strength indicators of the material. If you knock on a solid stone with a hammer, you can hear a long and quiet ringing sound.

Speaking about the types of rubble foundations, we can distinguish:
- Columnar bases — suitable exclusively for light structures, such as baths, greenhouses, sheds, light frame houses, and so on. Columnar bases are several pillars made of stone and installed at each corner of the building, at the intersection of internal and external walls. Such pillars are connected by means of a strapping grillage, which is the basis for the installation of walls.
- Ribbon foundations — suitable for residential buildings, both private and multi-apartment. Such foundations will be an excellent solution for structures that have a basement, and not a one-story, but a two- or even three-story structure. In addition, since the rubble foundation does not need additional reinforcement, it will cost much less than a base made of reinforced concrete material, especially if the quarry is located nearby.
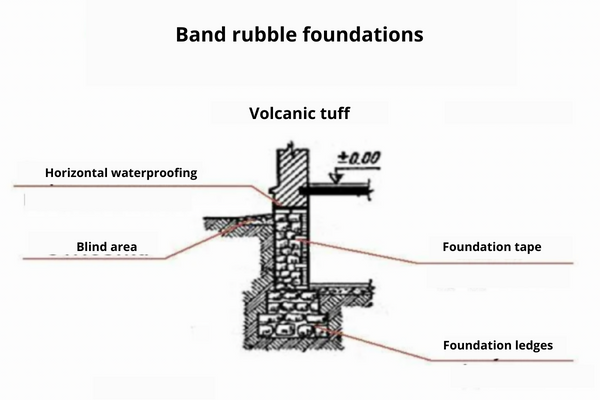
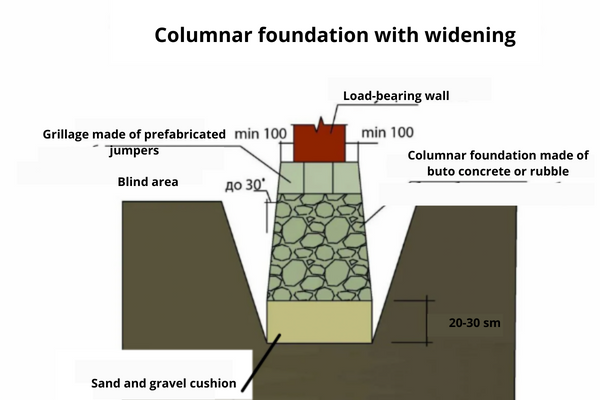
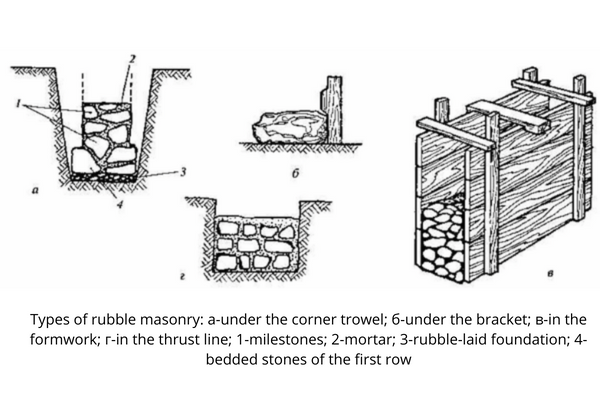
There are several main types of rubble masonry, which include:
- Laying of rubble “under the bay”: this technology is used in the formwork or between the sheer walls of trenches and involves laying the material with a parallel filling of cracks and holes with a special liquid solution;
- Laying of rubble “under the corner trowel”: in this case, the laying of rubble is carried out in horizontal rows on a solution with a fit of stones, all the voids are filled with crushed stone, and the seams are bandaged;
- Laying of the rubble “under the bracket”: this technology is practically no different from the previous one and is used during the construction of pillars and piers, and its only difference from the masonry “under the corner trowel” is the obligatory use of stones of the same height;
- Rubble masonry: the last type of laying of the material is the use of a mixture of concrete with the addition of rubble stones.
Methods of waterproofing rubble masonry and foundation
Various types of waterproofing are traditionally used for rubble masonry and rubble foundations. The most effective of them are considered to be injection and application of coating compositions. The choice of a suitable option depends on factors such as the dilapidation of the building and the presence of external and internal defects on it, the type of stone used for rubble masonry, the ability to make waterproofing from the outside or only from the inside, and others.
Injection of rubble masonry
Rubble masonry involves the use of uneven pieces of natural stone and is actively used almost everywhere, starting from the ribbon foundations of buildings and retaining walls and ending with bridges. Today but is not too often used for the construction of the foundation of multi-storey and high-rise buildings and country houses, however, such a solution can often be found in historical structures and buildings built more than 50 years ago.
The rubble foundation, especially if it has not been processed qualitatively, is often destroyed, which may lead to the threat of destruction of the entire structure or the formation of leaks. In case of violation of the integrity of the foundation, restoration and waterproofing works are carried out, which can be carried out by injection.
This technique is a technology for filling voids between the elements of the material through which moisture can penetrate with special injection compositions using a pump.
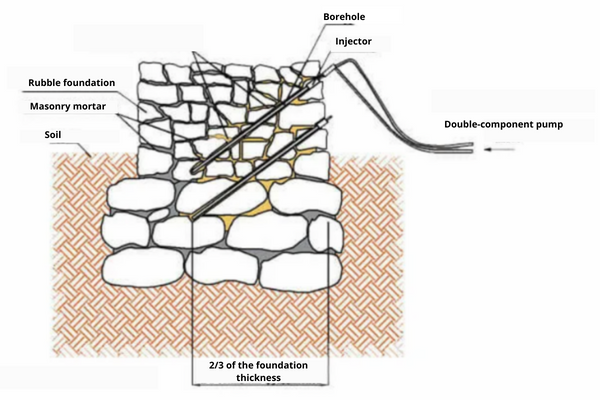
The main types of materials used to perform injection work:
- Micro-cement composition — is a cement-based bonding agent. Such material is able to fill the pores characteristic of concrete and stone, penetrating into all the voids of the base to a sufficiently large depth. There, the micro-cement composition expands, crystallizes, and forms a protective barrier that does not allow excess liquid into the room. Another feature of the composition under consideration is that it is sufficiently fluid and has the ability to penetrate even the smallest cracks. The index of its comprehensive strength exceeds the value of 80 MegaPascals.
- Limestone composition, among them, MAPE-ANTIQUE can be distinguished. This is an extremely fluid solution, which is considered to be volumetrically stable and has high resistance to the effects of chemical elements. This composition is used to strengthen foundations, arches, arched roofs, cement-containing elements of walls, and masonry, which are characterized by cracks and holes, as well as masonry exposed to groundwater and salts contained in the soil.
- Polyurethane elastic resins – these materials are usually double-component and have high fluidity, elasticity, and a high tensile coefficient, which makes them extremely effective for use as waterproofing compounds.
Important: Choosing the right material directly affect the effectiveness of the work performed and depends on the goals pursued and the quality of the rubble masonry. That is why it is recommended to entrust it to professionals.
The order of work on the injection of rubble masonry includes the following steps:
- High-quality cleaning of the work surface;
- Making holes straight or at an angle of 45 degrees (depending on the target) at a distance of 15-20 sm from each other;
- Packers connected to hoses are inserted into the holes;
- Pumps supply a prior prepared solution to the tubes;
- The material is fed, the gun is alternatively inserted into the holes, and a hydrophobic composition enters through it;
- Injection packers are removed from the base after the introduction of the material and its setting;
- After the composition is dried up, the final cleaning of the surface is carried out, and the injection sites are treated with cement mortar.
The use of injection at the construction stage or at the repair stage allows you to qualitatively and, most importantly, permanently protect the rubble foundation from the effects of excess moisture and water.
More information about the injection method of waterproofing can be found in the article – “Injection waterproofing”.
Application of coating waterproofing materials
A cheaper and therefore much more common method of waterproofing treatment of rubble masonry is the use of coating-type materials. In such cases, the foundation surface is covered with hydrophobic compounds that do not allow water to pass through, for example, bitumen mastics or mineral-acrylic materials. Such materials create a seamless surface, and also have frost resistance, resistance to temperature changes, and excellent adhesion to various substrates.
Important: Bitumen mastics do not work for negative water pressure, respectively, it is best to apply them from the outside of the foundation so that they work for clamping, not for separation. If the task is to make waterproofing from the inside of the room, then it is more correct to use materials that can withstand negative water pressure from the outside to the inside and that have 100% adhesion to the rubble, such materials are mineral-acrylic compositions.
Application technology:
The technology of applying coating materials is quite simple:
- Beforehand, the surface of the rubble foundation should be cleaned and dried.
- The material is evenly distributed over the work surface using a brush, roller, or spray gun.
- Waterproofing is applied in several layers, and each subsequent layer is distributed over the base strictly after the previous one has dried.
It is easier to work with coating materials in cases where rubble masonry is represented by bedded or tiled rocks, which are characterized by smooth edges. The coating waterproofing of irregular-shaped masonry is best performed with the help of specialists.
The rubble foundation is installed in a trench with a depth not less than the depth of freezing of the soil. The thickness of the foundation should be 12.5-25 sm greater than the thickness of the walls that will be installed after fixing the base. The first layer of rubble stone is laid out in a trench and filled with sand-cement mortar. After the solution dries, the second layer of rubble stone is laid, and it is important to ensure that as few holes as possible remain between the foundation elements. Only after the foundation is completely dry, its waterproofing treatment with coating materials is carried out.
You can read more information about the waterproofing arrangement of various types of foundations in the following articles:
- Foundation waterproofing arrangement: Methods, materials, prices, and recommendations of specialists
- Waterproofing of the ribbon foundation: Technology and materials
- Waterproofing of foundation blocks and walls
- Horizontal waterproofing of the foundation: The technology of the arrangement and the materials necessary for this
- Vertical waterproofing: materials and methods of its arrangement
- Waterproofing of basement and house walls from outside and inside – Methods, materials, prices, and technology
- Waterproofing of bricks and masonry
Prices for waterproofing arrangement
| Description of works | Unit of measurement | Price in $ |
| Arrangement of surfaced roll sheets | m2 | 39 |
| Arrangement of self-adhesive membrane | m2 | 39 |
| Application of mastic insulation in 2 layers | m2 | 40 |
| Application of liquid rubber in 2 layers | m2 | 40 |
| Application of cement-mineral 2-component mastic | m2 | 30 |
| The arrangement of polyurethane mastic | m2 | 60 |
| Application of cement compositions | m2 | 55 |
| Applying the primer | m2 | 5 |
| Description of works | Unit of measurement | Price in $ |
| Waterproofing of cold joints: – Works on the arrangement of the indenting – clearing the indenting – layer-by-layer sealing of non – shrinkable composition | running meter | 60 |
| Waterproofing of interblock joints: – Works on the arrangement of the indenting – clearing the indenting – layer-by-layer sealing of non-shrinkable composition | running meter | 40 |
| Waterproofing of deformation joints: – Works on the arrangement of the indenting – clearing the indenting – sealing of the elastic profile – sealing of non-shrinkable composition – a complex of works on injection | running meter | 490 |
| Injection waterproofing of seams / cut-off waterproofing – Works on the arrangement of the indenting – clearing the indenting – layer-by-layer sealing of non-shrinkable composition – Works on the arrangement of boreholes and installation of packers – a complex of works on injection – the dismantling of packers and sealing of injection holes | running meter | 120 |
| Injection waterproofing into the body of concrete marking, – Works on the arrangement of boreholes and installation of packers – a complex of works on injection – the dismantling of packers and sealing of injection holes | m2 | 190 |
| Injection waterproofing into the brick body -marking, – Works on the arrangement of boreholes and installation of packers – a complex of works on injection – the dismantling of packers and sealing of injection holes | m2 | 190 |
| Cement-mineral waterproofing | m2 | 60 |
| Penetrating waterproofing | m2 | 60 |
| Waterproofing of communication entry points: – Works on the arrangement of the indenting – clearing the indenting – layer-by-layer sealing of non-shrinkable composition – Works on the arrangement of boreholes and installation of packers – a complex of works on injection – the dismantling of packers and sealing of injection holes | piece | 690 |









