Table of Contents
- Types of different floor slabs and their type by purpose
- Why is waterproofing of floor slabs necessary and what are the consequences of its absence.
- Methods of waterproofing of concrete floors
- Prices for the waterproofing installation of floors
There are floor slabs in any structure of a house or building. These slabs are arranged horizontally, can withstand different loads and serve as the ceiling or floor of a certain room and have different purposes. These concrete elements need a certain type of waterproofing, even the interstory floors.
Types of different floor slabs and their type by purpose
Floor slabs differ in their type (location), as well as in the method of their construction and the materials from which they are made. Different types of floors require their own specific approach in terms of carrying out work to protect them from the effects of water and moisture.
In a private house with 2 floors, there will be either 2 or one overlap. If the house has a basement, then the first overlap will be between the basement and the first floor, the second floor overlap will be between the first and second floor and the third between the second floor and the attic or technical room in front of the roof.
Types of overlap by location:
- Attic floors – Located between the technical floor or attic and serve as the last line of protection of the main premises from water penetration if the roof has leaks. If the attic space is made in a private house, then the quality of life in the residential area of the attic and under it also depends on the quality of the slab.
- Interstory floors – Are a dividing structure between separate floors. Waterproofing of such floors is extremely important and not only in wet areas, as it is able to prevent water leakage from one room to another, standing below. Waterproofing of interstory floors is mainly relevant in multi-apartment residential buildings, where in the absence of high-quality waterproofing, a pipe break in wet areas (kitchen, bathroom) it can lead to serious consequences and flooding of neighbors.
- Basement floors and the slabs of the first floor- this element of the structure is located between the first floor and the basement. The task of covering the socle is to withstand future loads.
Types of overlappings according to the method of device and installation:
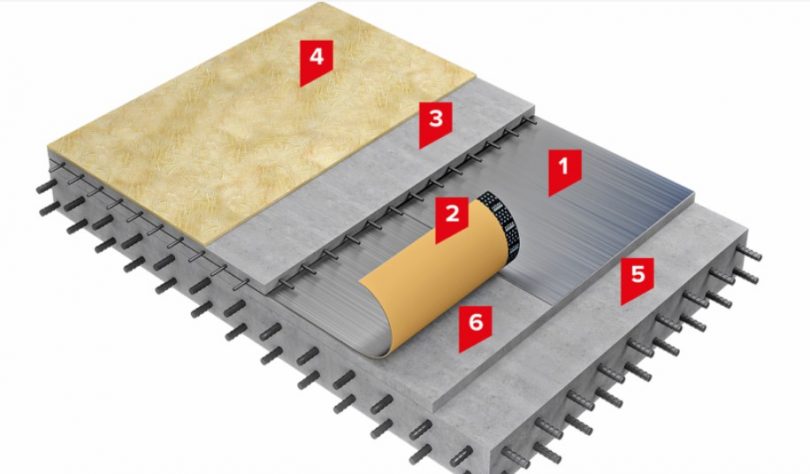
- Prefabricated floors -are divided into beam and slab. In the case of beams, the load-bearing beams are supplemented with concrete blocks and filled with a screed. When using slabs, ready-made reinforced concrete slabs are used. In brick and monolithic buildings, monolithic or large-format prefabricated floors made of factory multi-hollow reinforced concrete slabs are used in most cases, which makes them quite light. One of the biggest drawbacks of prefabricated structures in terms of protection against water penetration is the presence of numerous seams through which water easily passes.
- Monolithic floors – Unlike prefabricated slabs, a monolithic concrete floor has no seams and is poured at once onto a ready-made reinforced frame. The monolith filling is made of high-quality ready-mixed concrete and rests on the walls of the structure.
- Lightweight monolithic floors – Concrete is poured over a profiled sheet and as a result weighs less than a conventional monolithic slab.
- Filigree reinforced concrete slabs are a kind of middle option between a monolithic floor and a prefabricated one. These floors are made of reinforced concrete slabs, additionally reinforced with concrete and reinforcement. They are made independently directly at the place of work or ordered at the profile production.





Why is waterproofing of floor slabs necessary and what are the consequences of its absence.
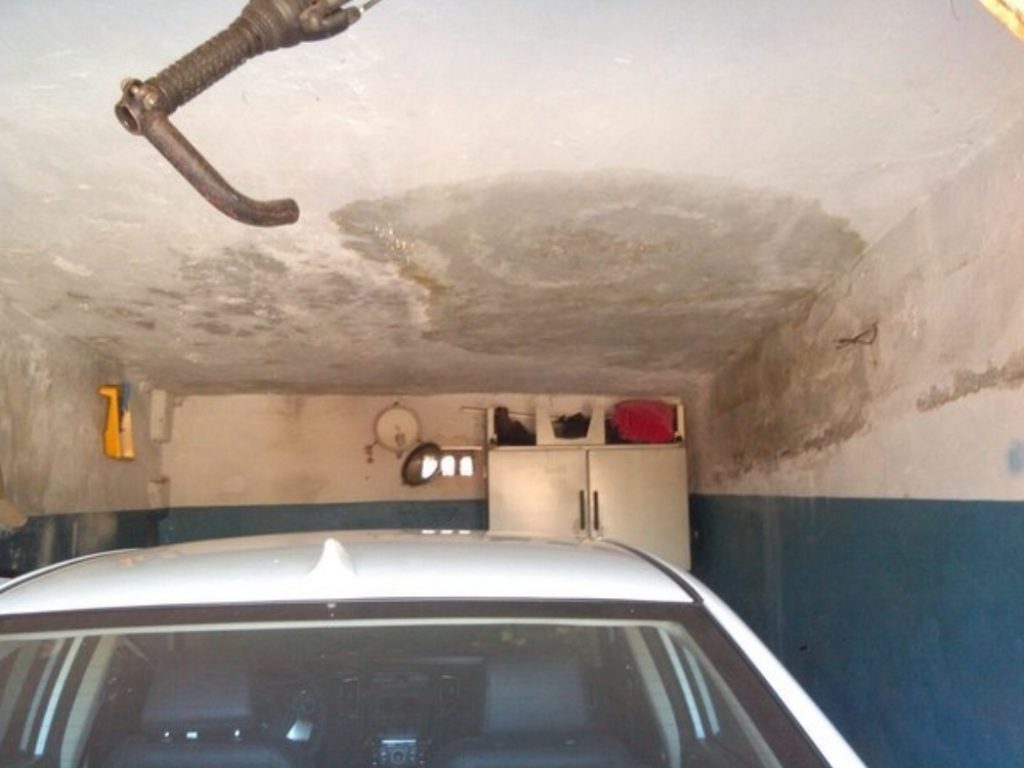
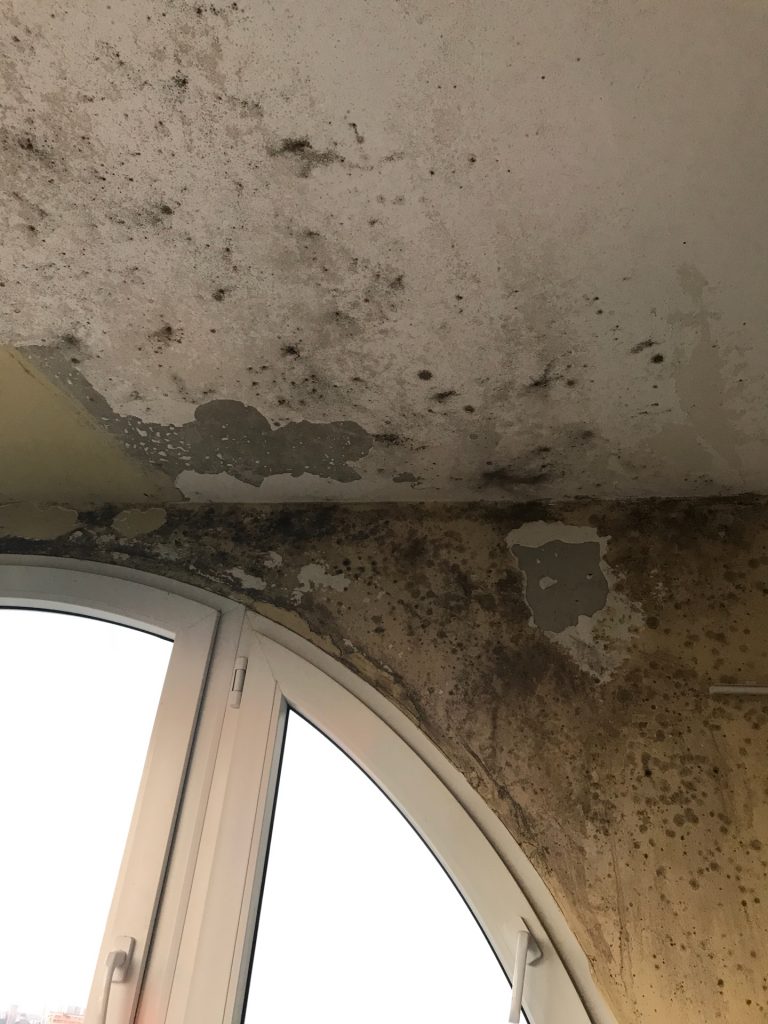
Monolithic and prefabricated floor slabs, like any other concrete foundation, can absorb water and moisture, and then pass it through itself. In the absence of high-quality insulation, water that has penetrated into the slab can penetrate into the living room located under it and thereby disrupt the finishing elements, damage furniture and flood the room on the floor.
Possible consequences in the absence of waterproofing of the floor:
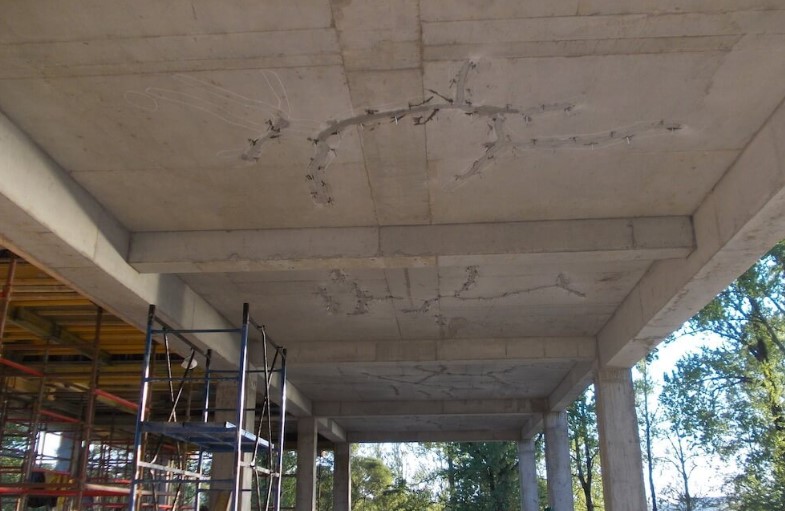
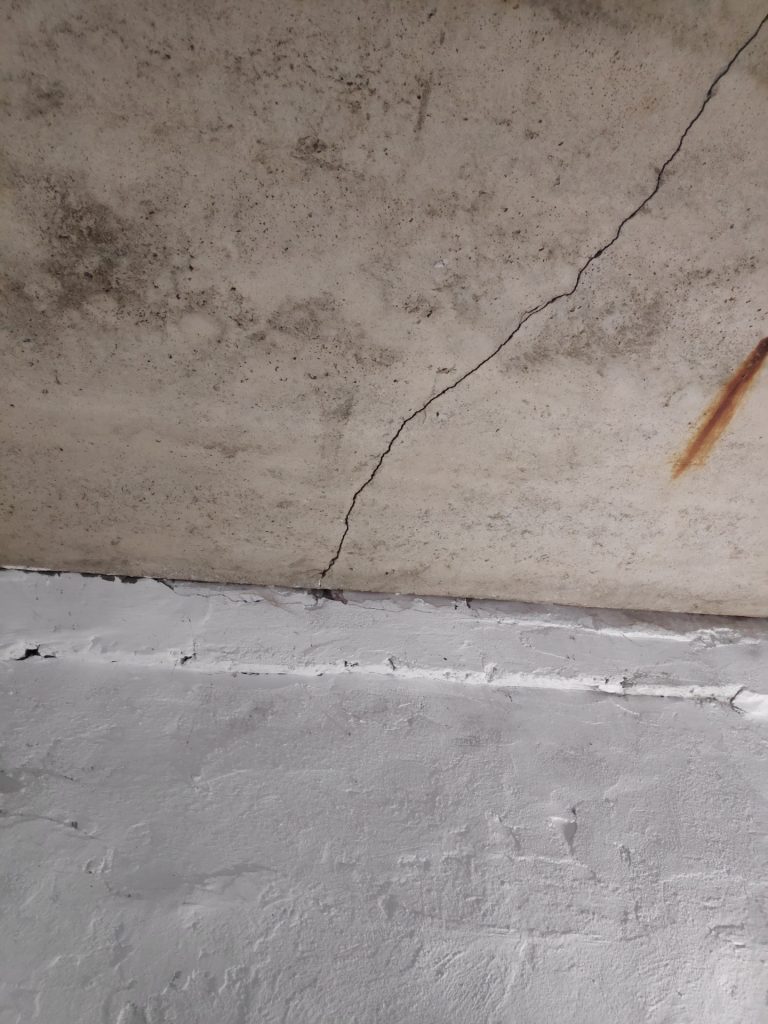
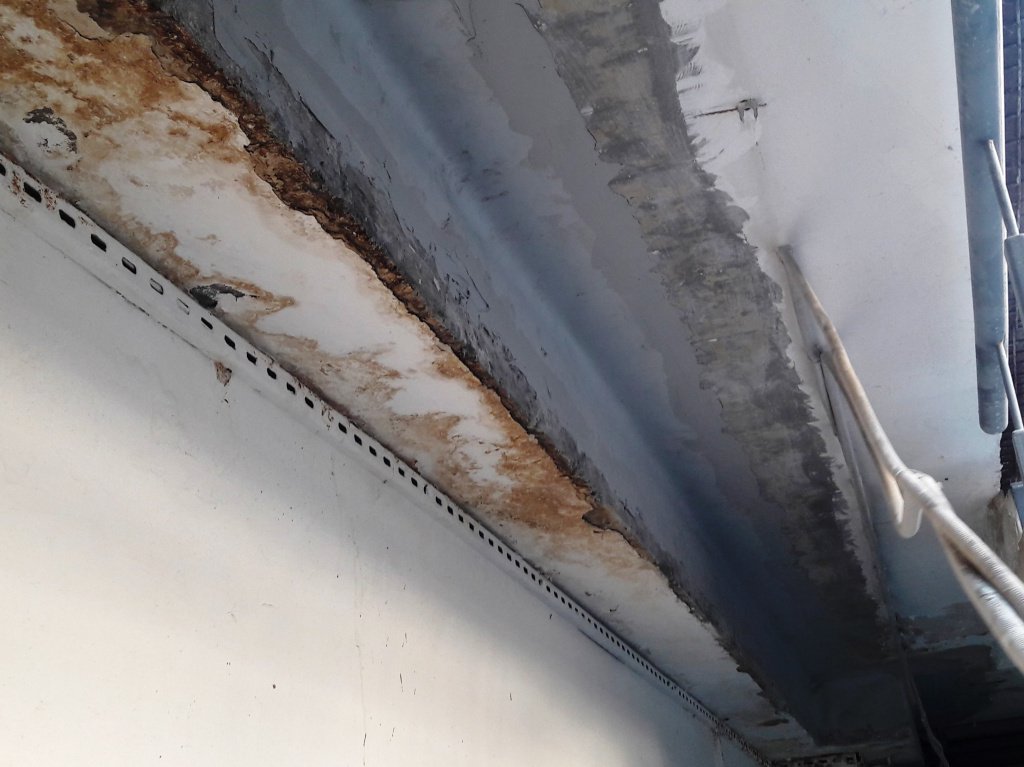
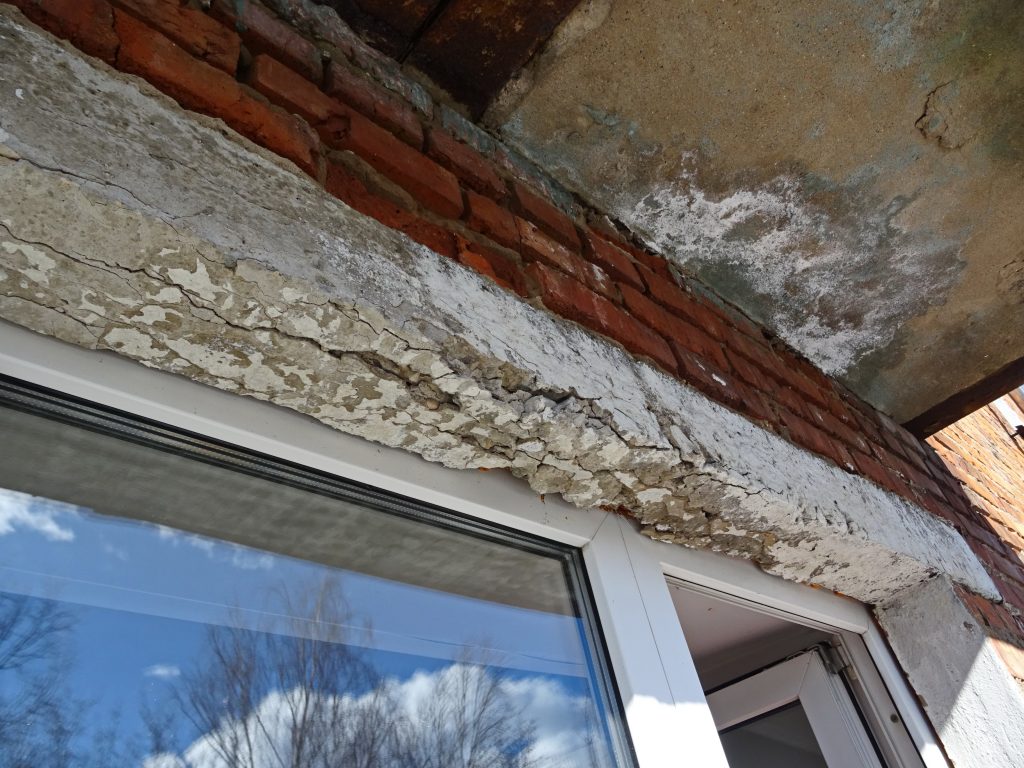
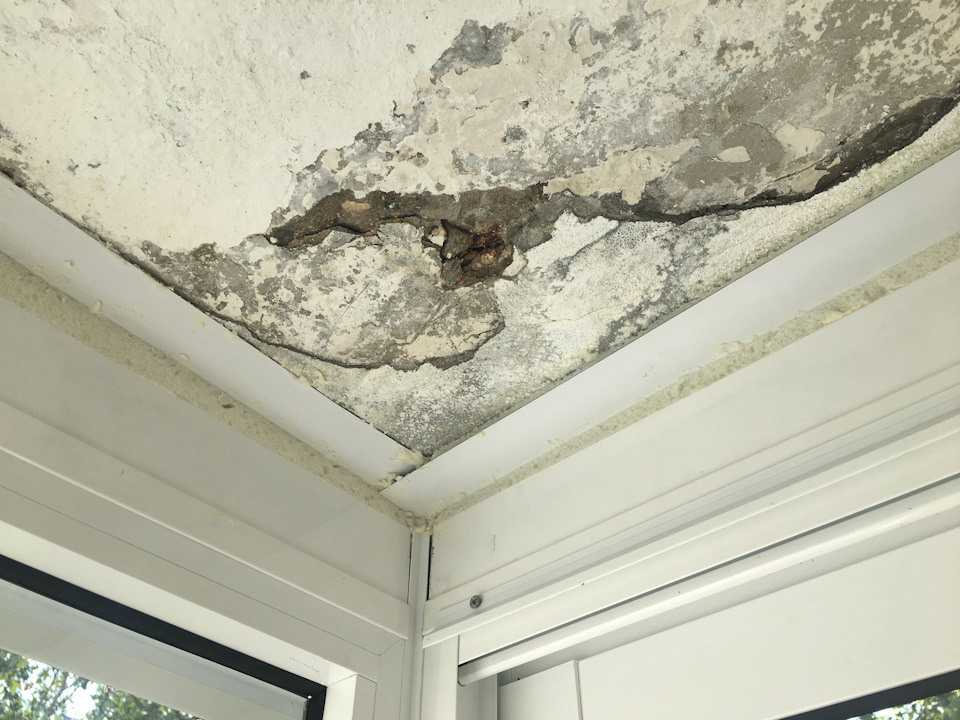
- Cracks and damages – If the ceiling borders on a street or a room that has no insulation, then in the presence of water or moisture on the surface of the slab, it is absorbed into the concrete base, freezes in winter and thaws in summer. Such a cycle of temperature difference breaks the concrete from the inside, forming microcracks, pores and voids, which increase every year.
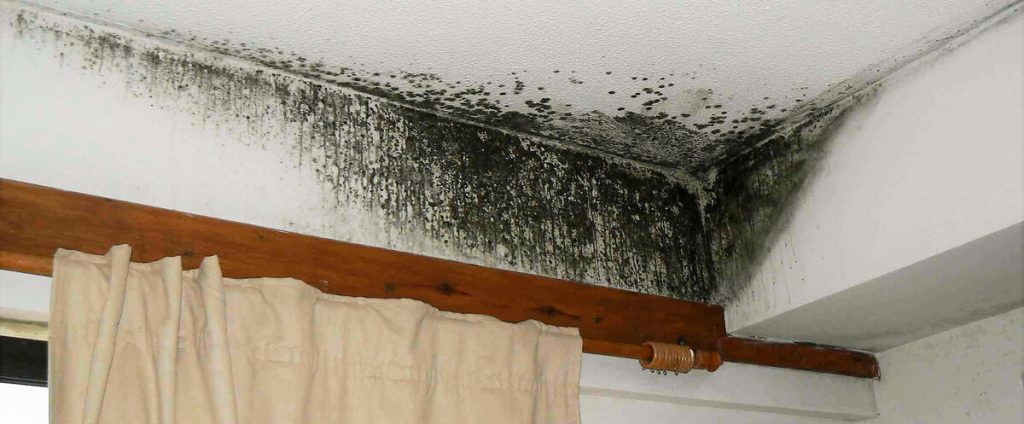
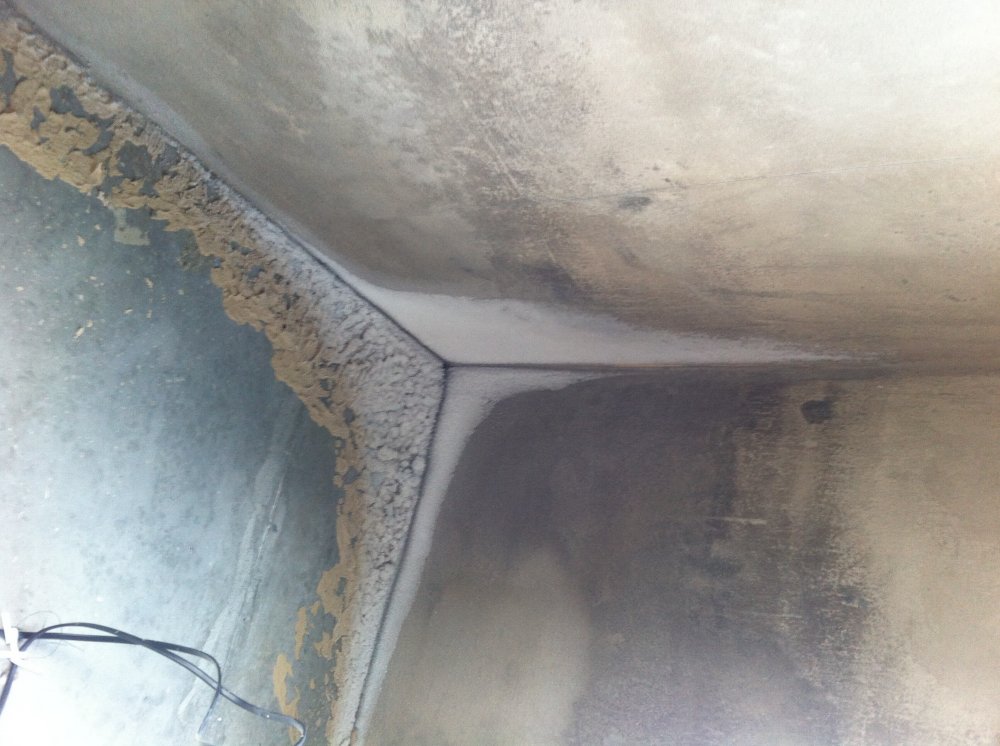
- Mold and mildew formation – Constant humidity in the room can be caused by water soaked into the floors. This state of affairs contributes to the formation of fungus and concrete mold that threatens human health.
- Active leaks through the slab – In the absence of high-quality protection, water can penetrate into a room that is not protected from water and harm the repairs made, furniture and appliances.










Methods of waterproofing of concrete floors
There is no ideal material for all occasions. The material for a reliable waterproofing installation should be selected based on the specific overlap and situation. For the right choice, it is best to invite professionals from among the profile companies whose specialization is directly waterproofing work.
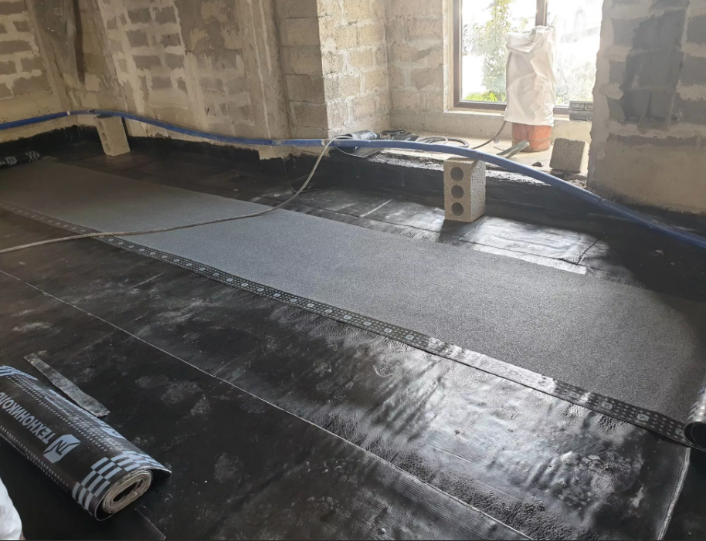
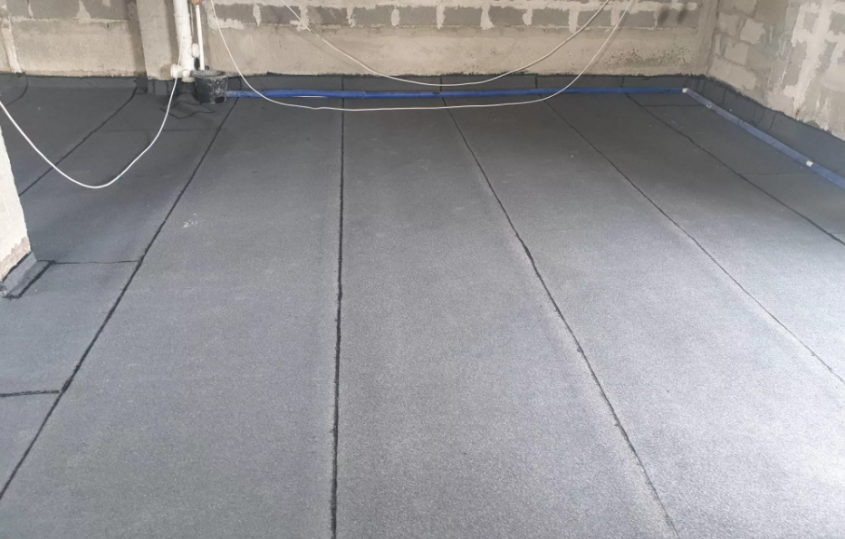
Roll-on surfaced insulation
This material does not work on the negative pressure of moisture and, accordingly, is placed on the outer side of the overlap, so as to work on the clamp. The rolls are deposited on the surface in one or several layers, depending on the type of deposited membrane. When surfacing, you need to use a burner and a propane-filled cylinder. Before performing the work, the concrete surface is primed with a bitumen primer.
In addition to the deposited rolls, you can also use various adhesive roll materials that do not need to be deposited with fire, since they have a special self-adhesive layer.
Despite the prevalence of roll insulation, the reliability of this material in terms of long-lasting protection against water penetration is questionable, mainly due to the abundant seams and joints formed in the coating during the installation of the surfaced roll membrane.
You can read more about roll waterproofing in the article – “Roll waterproofing installation with detailed installation instructions”.


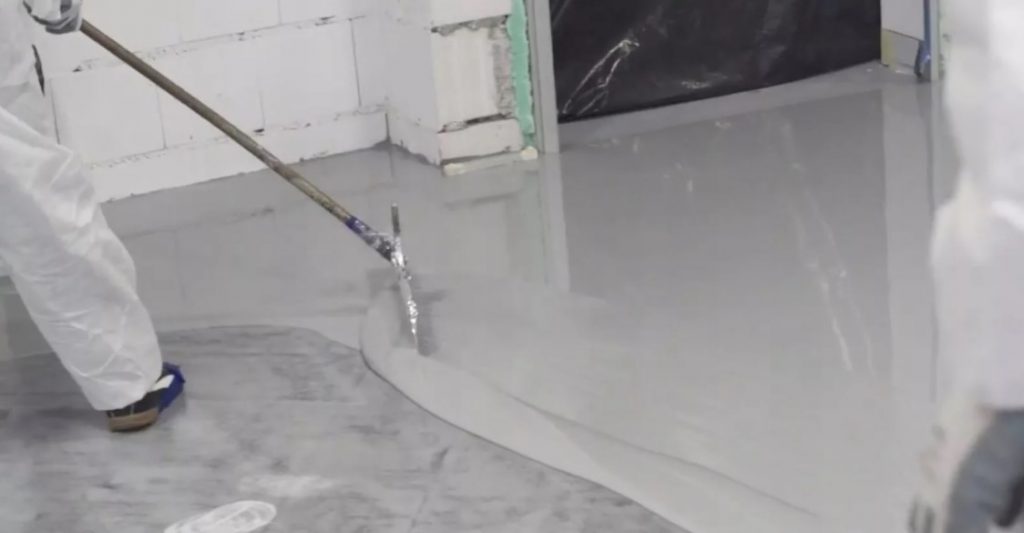
Coating insulation
Coating insulation is called various mastics that are applied to the surface by coating them using a roller or brush.
Coating mastics are applied in 1-3 layers depending on their characteristics. The coating insulation has several different options that differ from each other in the components from which they are made:
- Bitumen mastics – The main component will be modified bitumen.
- Polyurethane mastics – Polyurethane with various additives is used as a base. Polyurethane mastics can be both double-component and single-component.
- Acrylic – Made of various acrylic composites.
Polyurethane mastics are considered more reliable and durable than bitumen and acrylic.
When installing polyurethane waterproofing, a reliable layer of waterproofing is formed on the surface, without seams and with 100% adhesion to the surface, which makes this material ideal for both external waterproofing work and work related to waterproofing floors in wet and problem areas.
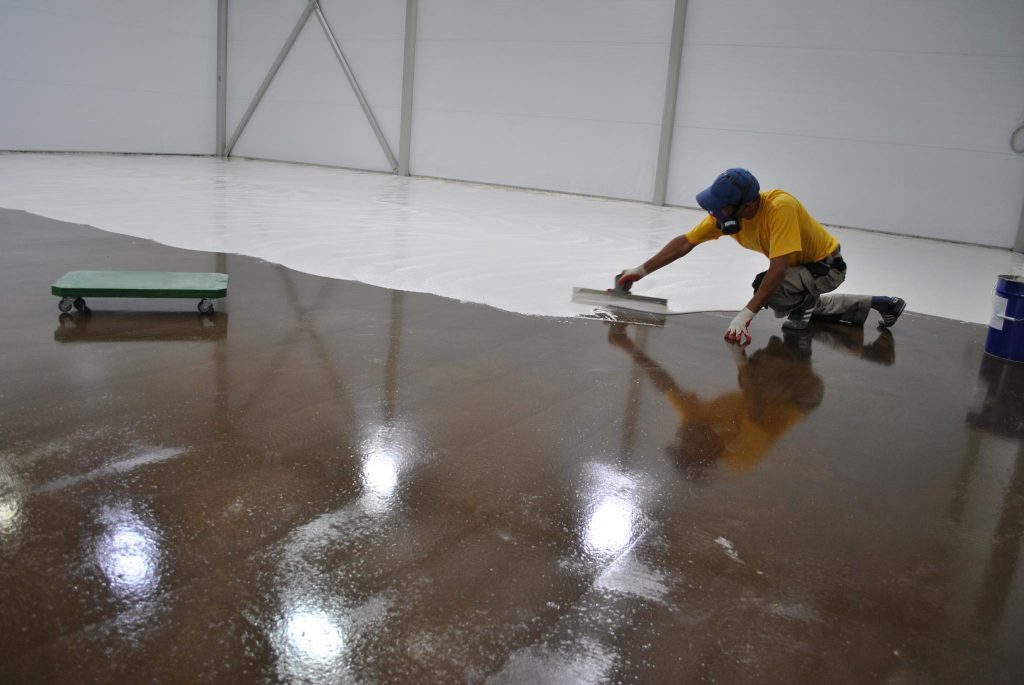
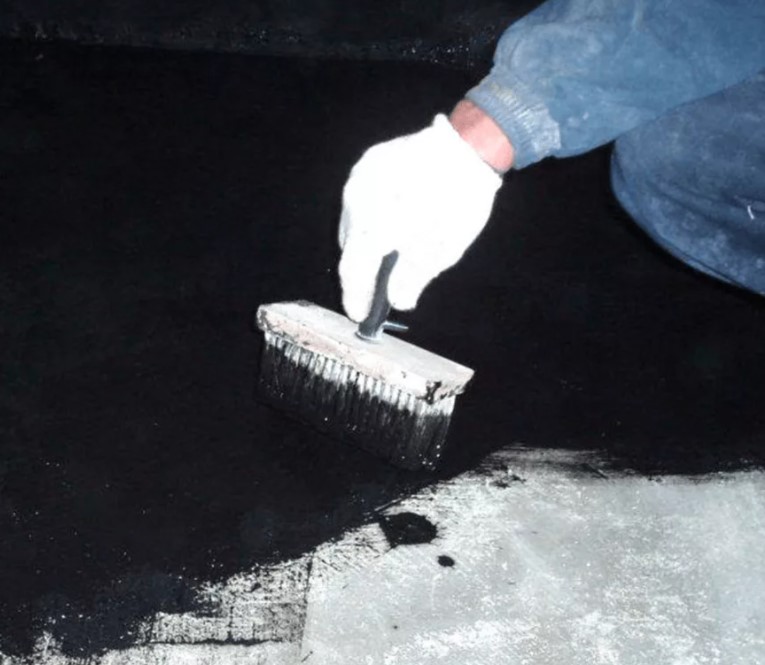
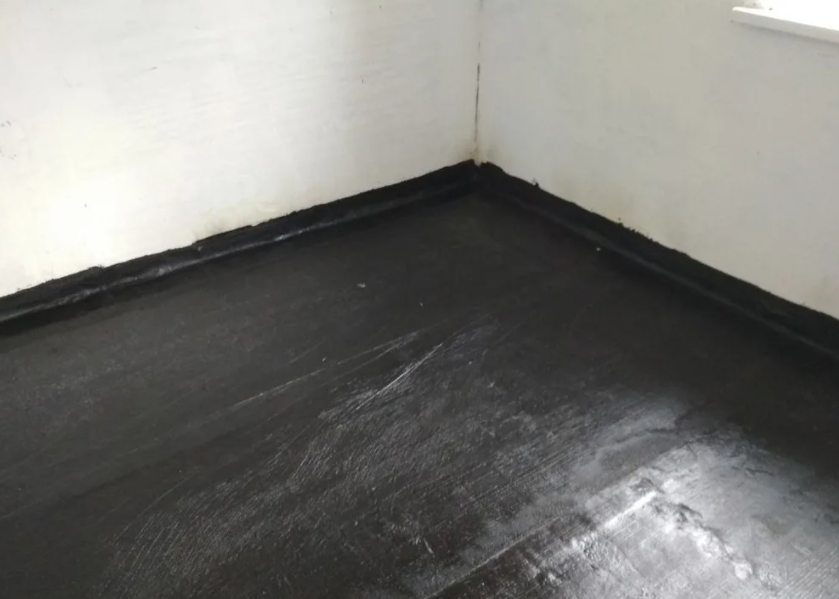





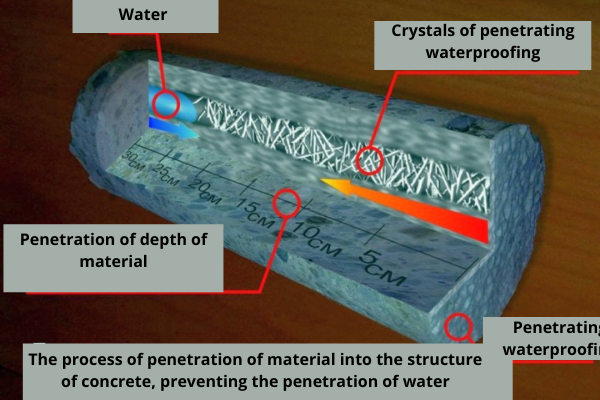
Penetrating compounds
Penetrating waterproofing is known for penetrating the structure of concrete. The penetration of the insulating compound into the concrete floor occurs due to the abundant moistening of the concrete surface before and after the application of penetrating compounds. Penetrating compositions mainly work on monolithic bases of slabs, since they cannot seal the void of the joints between the slabs, with a prefabricated version of the overlap.
If we talk about the protection of floors with the help of penetrating insulation, then this method is better used in cases where there is no access to the overlap from the outside, for example, when it comes to an interstorey overlap, where someone else’s apartment or room is located from the outside.
An excellent alternative to penetrating insulation will be special polymer-cement or cement-polymer materials working on negative water pressure, from the outside to the inside, such as HydroPaz Prime.
You can read more about penetrating waterproofing in the article – “Penetrating waterproofing: A detailed description of its work on concrete, types of materials and application technologies“.
Cement-polymer materials
These compositions are made on the basis of modified cements with various polymer additives. It is best to apply cement-polymer compositions with a brush or roller, while some materials react together with water or a second component.
When using such compositions in working with slabs of interstory and other floors from inside the room, it is best to use those materials that withstand negative pressure from the outside to inside, for example, HydroPaz Prime or analogues.
You can read more about cement compositions in the following article – “Cement-based waterproofing: Features, types and methods of its application”.
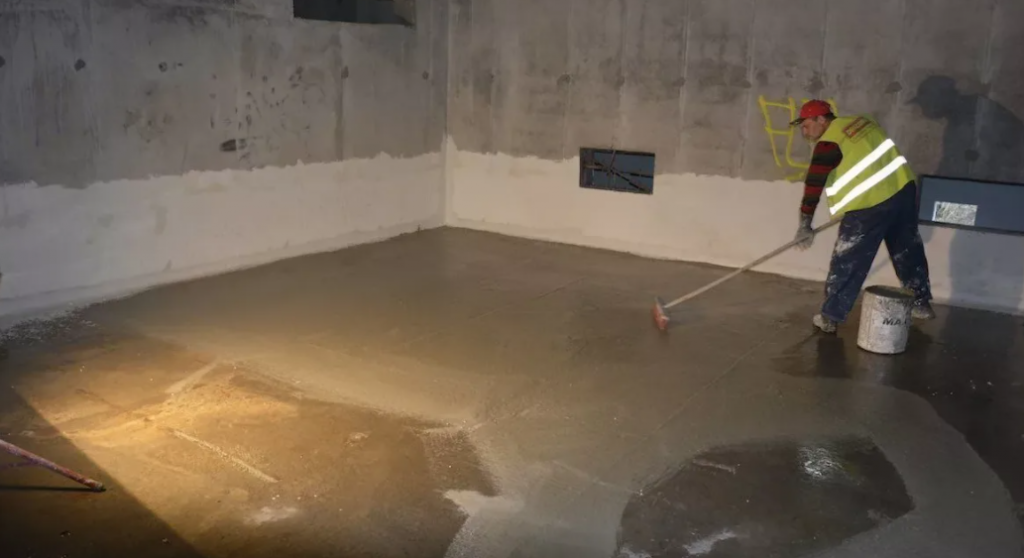

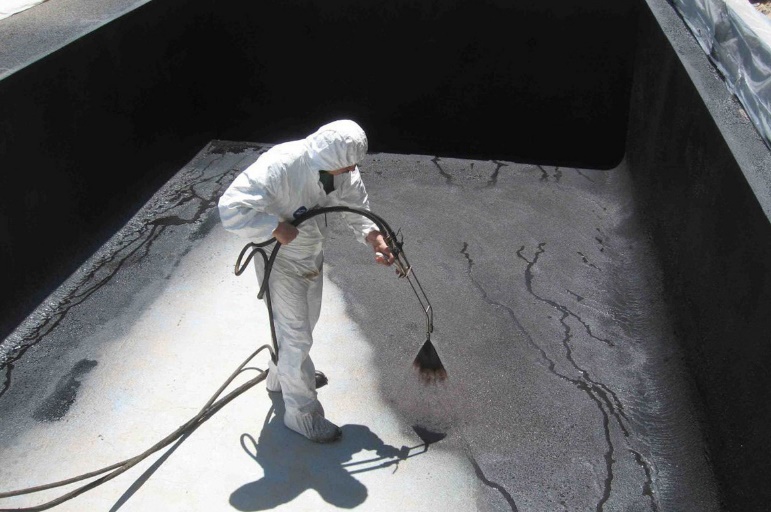
Liquid rubber
Liquid rubber is a sprayed waterproofing, but it can also be applied manually. The base of the liquid rubber will be modified high-quality bitumen and latex, giving the material elasticity and full adhesion to the base.
A quick and reliable way to make waterproofing. When applying liquid rubber, a coating is formed on the surface that has the following characteristics:
- No joints and seams;
- Stretching coefficient in 800%;
- Full adhesion to the base;
- Ecology.
The main advantages of the above characteristics are the absence of seams. It is the lack of seams and the elasticity of the material that makes it super reliable and durable in terms of protecting floors from water penetration, even under dynamic load and house movement.
You can read more about this material in the article – “Waterproofing with liquid rubber”.


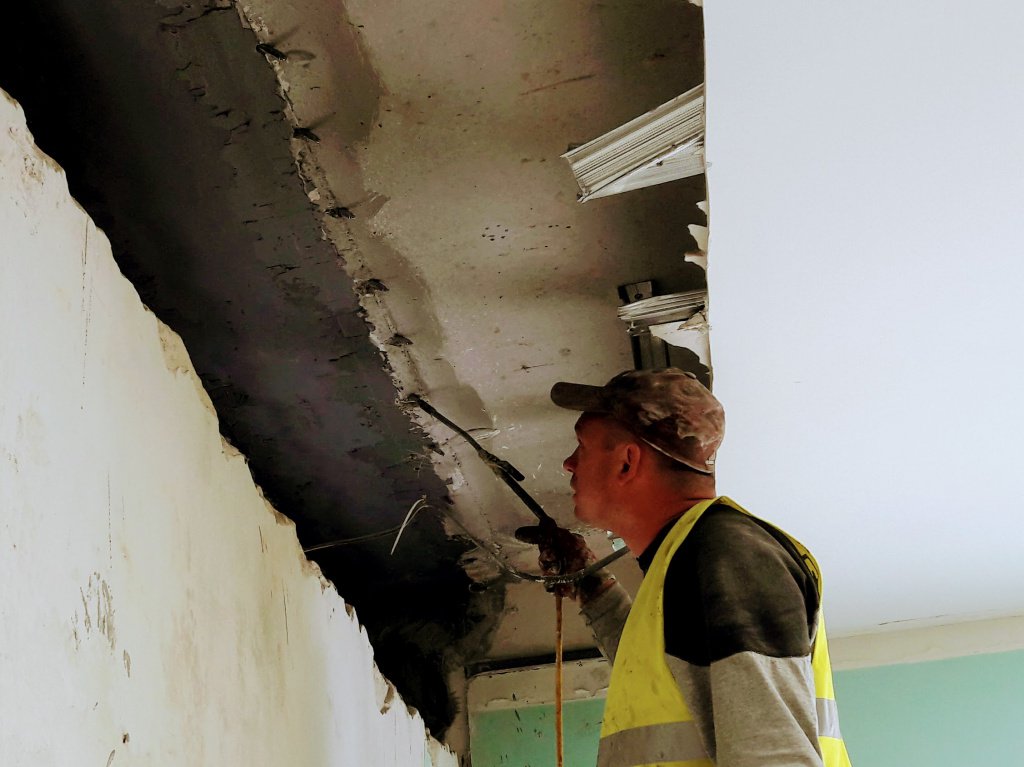
Injection waterproofing
Injection waterproofing is mainly used from inside the room, when there is no access to the outside of the ceiling, and waterproofing should be done. Injectable formulations have different modifications:
- Polyurethane compounds;
- Gel;
- Acrylate.
Each such composition has several varieties that differ in the following characteristics:
- Reaction time with water;
- Viscosity;
- The coefficient of stretching;
- Elasticity.
The selection of a particular modification depends directly on the design in which you need to make waterproofing and on the characteristics of leaks, if any.
Important: Injection is a difficult and responsible job that is best entrusted to a professional company with extensive experience in this field. Otherwise, the money can be spent in nowhere.
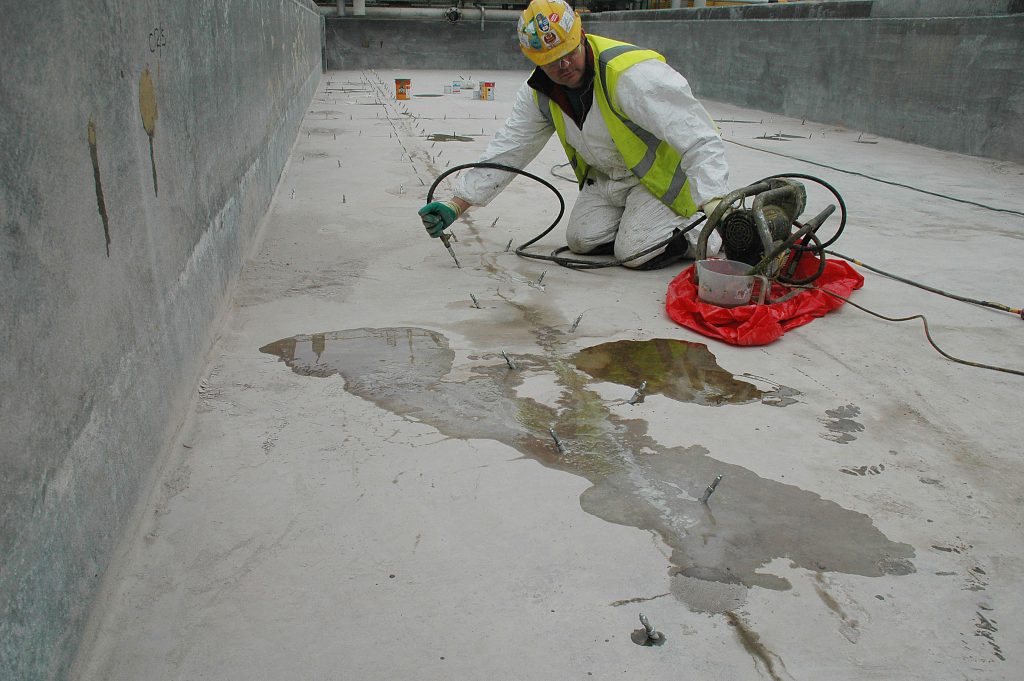
When working with slabs of various floors with the help of injection, the following important points should be taken into account:
- Waterproofing of cold, interplate and deformation seams – Seams are the weakest points in the overlap and it should be given special attention to them. Injection is excellent for reliable and long-lasting sealing of floor joints.
- Waterproofing of communication entry points – If pipes with communications pass through the slabs, then it is also recommended to inject these places.
- Waterproofing of cracks – In the presence of cracks in the overlap, they should be sealed by the method of their stitching, layer-by-layer sealing of expanding sealant and injection.
- Waterproofing of weak points in a prefabricated or monolithic floor.
Technology of injection waterproofing:
When performing an injection, a special polyurethane compound is injected using an injection pump into the body of the floor slab or various seams. Injection takes place through special injectors installed in the desired area. The material under pressure penetrates into all microcracks, pores and voids of concrete and expands inside, squeezing out moisture and making weak points in concrete hydrophobic.
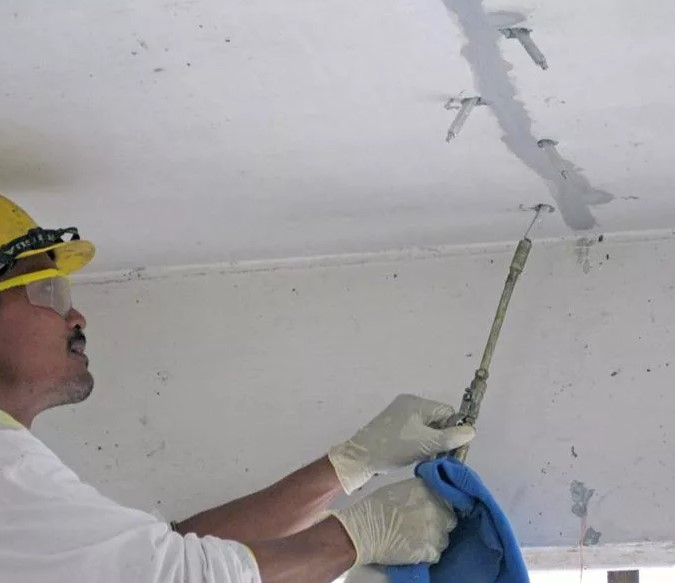





You can read more about this material in the article – “Injection waterproofing”.
The scheme of work of the injection material:
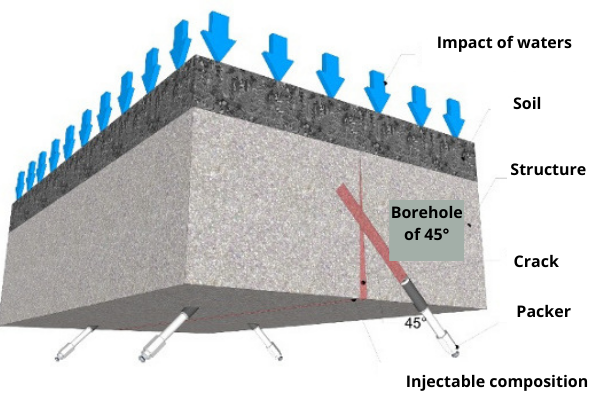
Table of comparisons between the main types of waterproofing
| Rolled: Surfaced Pasting Membranous | Coating: Bituminous Polyurethane Polymer-cement | Sprayed: Liquid rubber Polyurea Polyurethane 2К | |
| Coefficient of adhesion with the base | 0-10% | 100% | 100% |
| The availability of seams and joints in the coating | Available | Not available | Not available |
| Coefficient of elasticity and stretching | 10%-20% | 10-90% | 100-600% |
| Mounting method | Firing by means of a burner for surfaced membranes. Using a construction hair dryer for PVC membranes | Rollers, brushes, spatulas are used | Airless spraying equipment |
| Average productivity | 20-30 m2 per day | 100-180 m2 per day | 400-800 m2 per day |
| Complexity of repair | High | Low | Low |
| Actual service life | 3-6 years | 5-10 years for bitumen mastics 15-25 years for polyurethane | 20-35 years |
Prices for the waterproofing installation of floors
| Works description | Unit of measurement | Price |
| Installation of surfaced waterproofing in one layer | m2 | starting from 6$ |
| Installation of the pasting membrane in one layer | m2 | starting from 5$ |
| Installation of PVC membrane on the horizon | m2 | starting from 8$ |
| Application of bitumenous mastic in 1 layer | m2 | starting from 5$ |
| The installation of polyurethane mastic in 1 layer | m2 | starting from 4$ |
| Spraying of liquid rubber | m2 | starting from 5$ |
| Applying of liquid rubber manually | m2 | starting from 6$ |
| Application of polymer-cement mixtures | m2 | starting from 5$ |
| The arrangement of penetrating compounds | m2 | starting from 6$ |
| Primer coating | m2 | starting from 2$ |