Table of Contents
- Why is it necessary to do drainage and its design?
- Where should it is necessary to start designing drainage systems?
- What information is included in the drainage design?
- Types of drainage systems and features of their design
- Prices for drainage design
- Make a drainage project
The main task of the drainage system — is to divert both rain and ground water from buildings, private houses, foundations, various structures and sites. Therefore, how competently and technically correctly (observing all the norms) the project of this system will be drawn up directly depends on its effective operation over a long period of time.
In any area, even if it is located on a plain, moisture and rainfall are into the base of the soil. The amount of moisture is affected by various precipitation, as well as the presence or absence of groundwater.
The removal of water from the territories chosen for the construction of multi-storey buildings and private houses or for the arrangement of plots– is a process, that allows residential areas to get rid of problems associated with moisture exposure, which ultimately helps to project buildings and other structures installed on the ground from excessive mobility, leaks and destruction. How to design drainage properly, and what subtleties of the process should be familiarized with in advance?
Drainage, as a rule, is installed during construction:
- Private houses;
- Administrative buildings;
- Warehouses;
- Roads;
- Football and other playing fields;
- Capital structures.
Why is it necessary to do drainage and its design?
Drainage — is an engineering structure, designed to divert water from sites, various buildings and structures, such as:
- Foundation slab;
- Foundation in the form of a ribbon;
- Other foundation construction;
- Basement or socle walls;
- Football fields and other sports facilities;
- Roads;
- Swampy areas and plots.
Good drainage, made according to standards and technology, is necessary in order to:
- The completed waterproofing of the walls and foundation (if any) has lasted 5 times longer, since it will not be under constant water pressure.
- Reduce the fluid pressure on the foundation of the house, which, if there is a basement or socle, will help reduce the volume of leaks and their intensity.
- Prevent the destruction of concrete and foundation. In the absence of drainage and high-quality waterproofing, under the constant influence of moisture, the foundations of concrete, brick and other materials are gradually destroyed.
Concrete and brick are porous substances that absorb water like a sponge and are destroyed both from the effects of minerals and salts present in ground water, and from the temperature difference – at minus temperature, moisture that has absorbed into concrete freezes, and at plus temperature thaws, thereby forming cracks, capillaries and voids in concrete.
Drainage helps to remove excess moisture from the foundation of concrete or other material and thereby significantly improves the situation and helps the foundation to last longer. - Prevent permanent erosion of the foundation, which can eventually lead to cracks and dislocations.
- To save a site or a certain territory from constant waterlogging and the inability to operate it at certain times of the year.





Why it is necessary to prepare a design before implementing the system:
- To understand in advance at what depth and where the drainage structure will take place, so that the builders do not make a mistake and do not perform work a mistake and do not perform work, where it is absolutely not necessary to do it;
- Have a complete idea of what materials, according to the norms, an engineering structure should be made of;
- Have a detailed guide and recommendations for drainage installation around the house, structure, building or plot;
- Get an accurate specification of all materials used;
- Get accurate prices for the installation of the system, taking into account all the necessary work and materials.
Where should it is necessary to start designing drainage systems?
First of all, it is important to get complete information about the area, the drainage of which is planned to be performed. It is necessary to have an idea of the following nuances:
- Geology – determining the depth of each layer of soil and aquifer.
- Topographic survey of the area to determine the height differences and future slopes of both the engineering structure and the discharge channel.
- The nature of the soil in the selected area – Clay, loam, sand and etc…
- The level of soil freezing.
- Groundwater level – When they do not accumulate and do not stand on the surface of the earth, simpler technologies can be designed, and the installation of a drainage system will not be associated with water reduction and other difficulties.
- Availability of a place for the discharge of diverted water, for example, a village storm sewer, a wasteland, a ditch, a forest plot, etc…
If you already have a drainage system installed and you need to understand how well it works and whether it works at all, then you need to perform an examination of the existing structure before starting the design work.
You can read more about the examination in the following article – Construction examination of the drainage system, its inspection and testing.
What information is included in the drainage design?
The drainage system design is actually and extremely voluminous document that includes many subtleties and details. Here are some of the items that should be included in the standard project documentation:
- General plan of the drainage and discharge system with indication of slopes and water flow;
- General plan of the storm sewer system with indication of water flow;
- General explanatory note with detailed guidance and description of special places and conditions;
- Sections along the pipeline line taking into account the structure of the site;
- Tables of wells / profile;
- Design of the pumping station (if available);
- Design of the extinguisher well;
- The design of the reset channel;
- Specification of materials;
- Statement of work and management;
- Estimated calculation.
If necessary, the project documentation is supplemented:
- Topographic survey
- Geological surveys
Further you can learn more about some of the points.
System location
When designing drainage, it is important to provide exactly where it will be located and the final destination. The conditions for the design of structures for multi-storey buildings and for private houses may differ significantly from each other. In urban conditions, it is important to take into account the location of roads to the planned drainage system and urban storm sewer.
Example of a design solution:

Slopes and depth of laying
Depending on the purposes of drainage and the characteristics of the territory, the project should take into account a certain slope of the future structure. Also, an important factor is the depth of the drainage. It is determined, by the project depending on the purpose of the system.
For example, if the purpose of drainage is to protect the basement of a house from pressure and moisture, then it should be installed below the base plate, so that it takes not only the water that comes to the building, but also the water that is under it (under the foundation).
Elements of the drainage structure
The composition of the project, as a rule, includes numerous elements, the number and composition of which depend on the requirements for a particular area. Such elements include. For example, drainage plans, open or closed drains, as well as wells of various types and purposes.
Wall-mounted, linear and annular drainage systems are characterized by the arrangement of trenches, inside which the filtration material and the drainage pipes themselves are located.
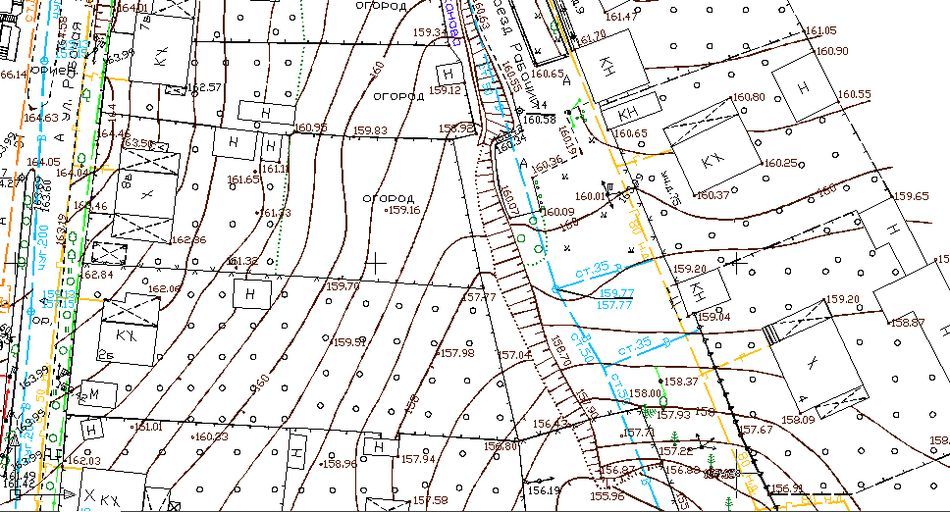
Topographic map of the area
When drawing up a project, it is extremely important to understand the nature of the terrain, the slopes and the possibilities of diverting water from the desired area.
The designation of relief marks will help to understand how realistic it is to carry out drainage from a well into a ditch or a storm system by gravity, or for this you will need a special pump that removes water from the collector forcibly (since there is no way to reach the desired level according to the slope marks).
Example of a design solution:
Communication scheme
The project should reflect not only the drainage itself, but also the communications taking place in the work area. Modern communications, both above-ground and located underground, can become a serious obstacle to the installation of future drainage structures. Therefore, at the design stage, a detailed communication scheme is drawn up, providing for the passage of electric wires, gas and other parts of urban or village communication, if we are talking about a private cottage or house.
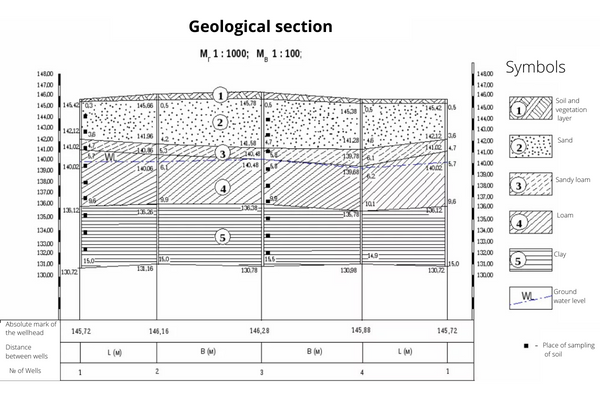
Hydrogeological features of the area
The last, but no less important point in the project is the study of the geology of the area, as already mentioned above. The nature of the soil, the occurrence of groundwater, aquifer, sand layer, etc. It is important to understand that with high ground flows, for example, at a depth of 1.-1.2 meters from the zero level, the drainage installation can be extremely difficult, since when performing ground work to a specified depth, the trench will be filled with water and perform work it possible only after the installation of a special construction water treatment.
Example of a design solution:
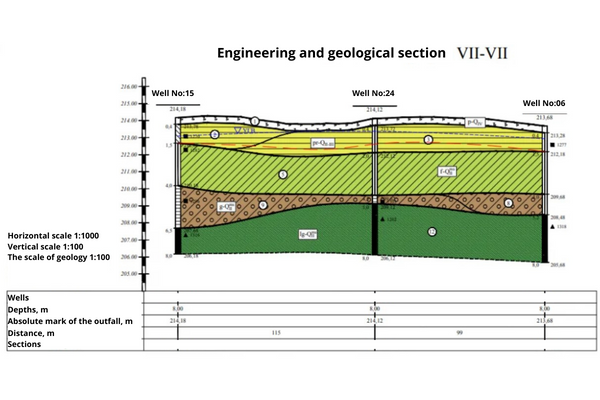
Types of drainage systems and features of their design
Drainage systems, like any other object of modern construction, are divided into several types, each of which has its own purpose, its own subtleties and features. What types of drainage are common today?
In addition to installation, at the stage of designing the timing of drainage, it is also important to determine the type of drainage system. To date, surface and underground installations are distinguished. Vertical, horizontal and combined technologies of underground drainage are also used in the design of drainage.
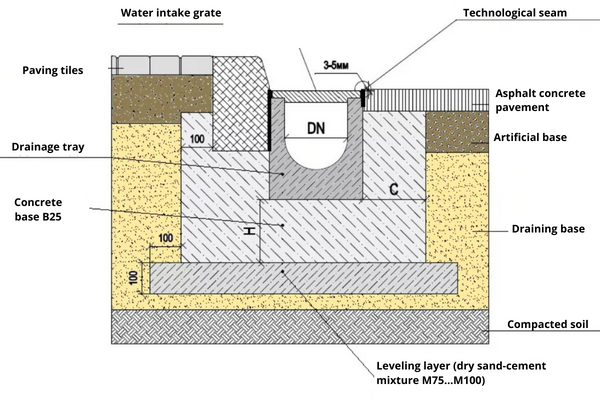
Surface:
Used in cases, where it is a question of diverting not only the upper reaches of when soils have low permeability. Surface drainage and drainage systems collect and divert water from the territories adjacent to the building or site. This is achieved by draining into channels or wells. This type of structure is laid to a depth of no more than one meter.
Design scheme of the surface solution:
Deep or underground:
Underground or deep drainage systems are characterized by a more complex structure. They are used to protect foundations buried more than 1 meter deep or located near groundwater, reservoirs, in lowlands or in areas with clay soils. This type is also used to protect premises located underground.
The design scheme of the deep solution:

Vertical:
The vertical system involves the installation of wells at a depth of 20 to 50 meters. The water first flows into them, and then is pumped out to be discharged into a special water-absorbing layer.
Design scheme of vertical installation:
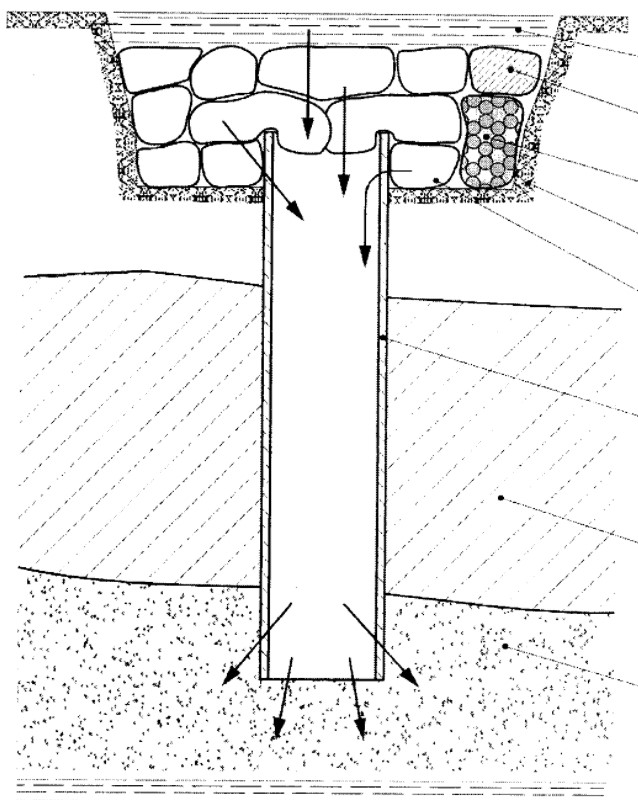
Horizontal:
Horizontal options include the use of trenches, in which pipes are located that send the collected water to nearby wells. The combined technology includes the use of both horizontal and vertical elements.
Resevoir:
In most cases, the solution is designed at the construction stage of the building, since it is located under the building itself and is intended to divert water precisely from under the slab of the building or other structure.
Design scheme of the reservoir installation:
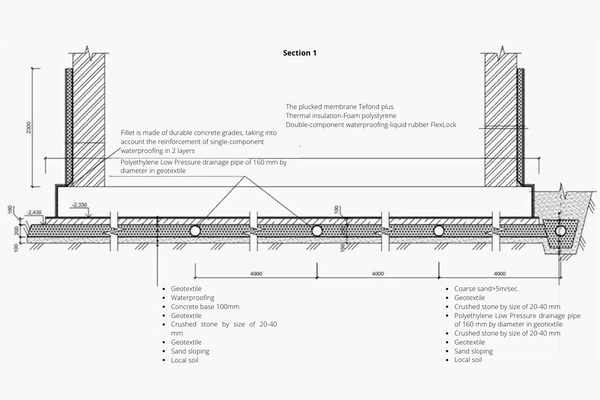
Design of wall drainage
Wall drainage — is the drainage that is installed close to the foundation or foundation walls. Its task — is to divert water from the existing basement, socle or foundation as efficiently as possible, preventing water from being in the area between the ground and the wall and affecting the base of the walls or foundation. As a rule, wall drainage is designed where there is a basement or socle room to prevent moisture from affecting the foundations and its penetration into the room.
Important: Drainage cannot completely solve the problems with leaks in the basement of the house, these problems should be solved by high-quality waterproofing. Drainage is not waterproofing, drainage — is an auxiliary system that weakens the water pressure on the structure, so that the performed waterproofing lasts 5 times longer.
A well-designed and performed drainage saves the structure even from deformations due to the displacement of the soil layers relative to each other.
What is not worth doing when designing:
- The arrangement of enclosed areas near buildings cannot be carried out without first removing water from the territory.
- It is not recommended to ignore such important elements as the system of drains and storm sewers. At the design and planning stage, it is important to draw up a complete scheme of them.
- If retaining walls are fixed in the ground, or communications that hinder the performance of work, they should be reflected in the design.
- When developing design documentation, it is not necessary to ignore the presence or absence of high groundwater. If they are available in the project, it is necessary to take into account the construction water supply when performing work.
Design scheme of wall drainage:
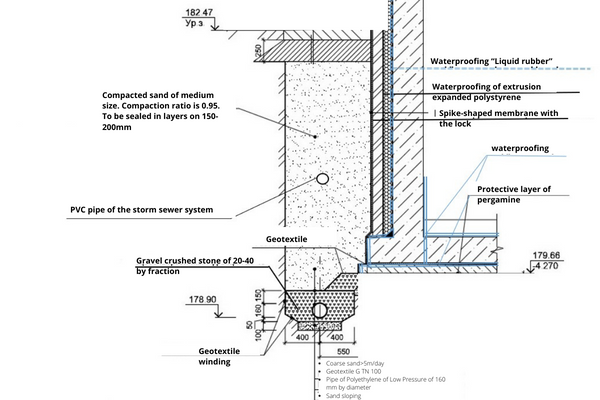
Foundation drainage design
The accumulation of groundwater can interfere not only with life in an apartment or private house, but also with the constriction of this house itself. Therefore, often the design and installation of foundation drainage are carried out even before the construction of a building or structure. Drainage of water from the foundation is carried out using systems of channels, wells, pipes and collectors.
The presence of moisture in the ground can negatively affect the integrity of the structure not only in the warm, but also in the cold season. The accumulation of liquid inside the soil as a result of rains and floods leads to the fact that in winter this liquid freezes and provokes soil displacement (heaving).
And they, in turn, become the cause of the inevitable destruction of the building. Therefore, the preliminary removal of moisture from the house or plot is considered one of the main points in the arrangement of the territory and the design of buildings, foundations and houses.
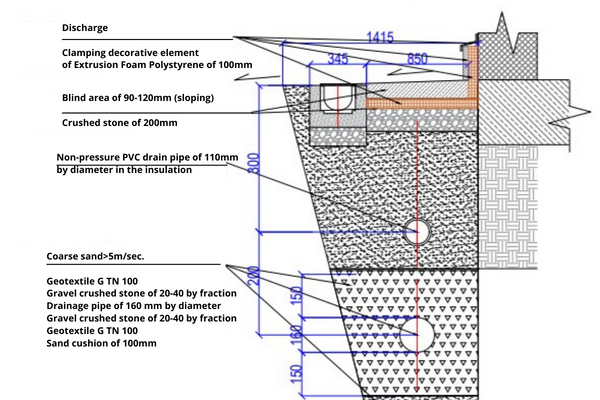
Sire drainage design
Designing a drainage structure for a site can be attributed to ne of the most important tasks.
To install a drainage system on a site, you first need to draw up a detailed diagram of the territory and all the details of its arrangement, not to mention such classical knowledge as understanding the hydrogeological features of the territory and its topography. Moreover, a country plot may be located on a slope or in lowland, which somewhat complicates the installation of a drainage system, so information about this should necessarily be included in the design.
In most cases, the plots are equipped with open or closed drainage systems. The first are located on the earth’s surface and represent a system of ditches, trenches and small wells. Closed systems are fixed underground and incline pipes, various channels, drainage materials and other elements.
Design scheme of open drainage:

Design scheme of closed drainage:
Recommendations for the design of drainage systems and the most common mistakes of designers
- Error: Filling the drainage completely or half with soil, loam, clay, or dirty quarry sand.
Recommendation: Soil, quarry or dirty sand has a low throughput coefficient, due to which water stagnates on the surface or slowly absorbs into the base, that is why drainage simply does not work or works at 10-15% of its real capacity. The drainage should be filled to the top with draining material, through which the water passes like through a sieve, getting into the perforated pipe as quickly as possible, which, thanks to the slope, will quickly take it away. Backfilling should be done with crushed stone or sand washed large, it is through these materials that water passes quickly, unlike soil or dirty sand. - Error: Install wall, ring or deep drainage flush with the foundation plate,
Recommendation: When installing wall drainage flush with the foundation, the system will take over only the water that approaches the building or basement along its perimeter, but at the same time the water under the building will not get into the drainage, but will continue to soak into the base plate destroying the foundation and forming leaks in the basement (mainly in the locations of cold seams– the abutment of the plate and the wall). Wall drainage around a house or building is recommended to be installed below the level of the foundation so that it can take over the water that comes to the house and the one that is under it. - Error: Install drainage, bring it into the collector (well), but do not take care of the discharge channel.
Recommendation: In the absence of the discharge channel, drainage water will overflow the collector very quickly and go backfilling the drainage prism and standing in it, increasing the water pressure at the bottom of the foundation, which can increase the negative effect and leaks in the basement if there is one. It is necessary to take care of the discharge channel from the collector outside the site, into the forest, wasteland, urban or village storm sewer or trench. - Error: Dumping streams from the roof drainage system into the drainage.
Recommendation: Due to the large flow of water from the roof, such a step can overload the drainage, as a result of which its efficiency will greatly decrease. Accordingly, the storm sewer system should be started separately in its own PVC pipe channel. - Error: Design and installation of drainage and discharge system without installation of inspection wells.
Recommendations: Without inspection drainage wells, you will not be able to inspect and maintain the completed system. In case of silting up or malfunction of the system, it will have to be completely excavated to perform repair work. If you do not want to bury the work you have done, it is recommended that you first add to the project and then install inspection wells at the main corners and turns, as well as every 20-30 m (in a straight line) through which in the future you will be able to inspect the system and, if necessary, punch and clean it, for example, using a hydrant and high pressure.
Prices for drainage design
The prices for the development of the design documentation directly depend on the amount of work, the complexity of the design and what exactly the design will include. Below are the average prices for the development of the project, and they may vary depending on the specifics and tasks of a particular case.
| Description of work | Prices in $ |
| Drainage system design superimposed on the geo-base | starting from 1200 |
| Development of design documentation for the drainage installation, which includes the following sections: 1. General plan of drainage system with indication of water flow; 2. General plan of the storm sewer system with indication of water flow; 3. Explanatory note describing special places and conditions; 4. Sections along the pipeline, taking into account the structure of the site; 5. Table of wells / profile; 6. The design of the pumping station (if available); 9. The design of the dampener well; 7. The design of the water discharge channel; 8. Specification of materials; 9. Statement of works; 10. Estimated calculation | starting from 1600 |
| Draft drainage system, storm sewer system, waterproofing and thermal insulation of the foundation below the level of 0.00 1. General plan of drainage system with indication of water flow; 2. General plan of storm sewer system with indication of water flow; 3. General explanatory note describing special places and conditions; 4. Section of the foundation structure with indication of the waterproofing unit; 5. Section of the foundation structure with indication of the thermal insulation unit; 6. Sections along the pipeline, taking into account the structure of the site; 7. Table of wells / profile; 8. The design of the pumping station (if available); 9. The design of the dampener well; 10. The design of the water discharge channel; 11. Specification of materials; 12. Statement of works; 13. Estimated calculation | starting from 2400 |
| Storm sewer system project 1. general plan of the storm sewer system with indication of water flow; 2. General explanatory note describing special places and conditions; 3. Sections along the pipeline taking into account the structure of the site; 4. Table of wells; 5. Design of the pumping station (if available); 6. The design of the water discharge channel; 7. Specification of materials; 8. Statement of works; 9. Estimated calculation | starting from 1600 |
| Preparation of Work Production Project (ППР) | starting from 800 |
| Geological surveys (add a section to the project) | starting from 500 |
| Topographic survey (add a section to the project) | starting from 800 |
Calculator of the cost of development of the project documentation for online calculation
Разработка проектной документации по устройству дренажных систем и водоотвода
Итоговая стоимость разработки проектной документации
Calculator of the cost of works on the installation of drainage structures
Calculation of the cost of drainage systems
The total cost of the drainage system
If you are interested in more detailed information about the installation methods of various drainage systems and prices for these works, then by clicking on the link you can get acquainted with the necessary information: A turnkey drainage installation around the house: Proper drainage, its types, installation technologies, materials, schemes and prices.
Make a drainage project
You can either do the design yourself, or entrust this responsible process to specialists. Representatives of professional companies will be able to provide the customer with a detailed and concise scheme, a guide for its installation, reports on the study of the area, a list of materials that are best suited for a specific situation, the composition of the system in need, the stages of work on its installation, as well as explanatory notes to technical issues, a work plan and other necessary instructions and design sections.
Large companies annually carry out dozens of different projects for drainage, discharge and storm water systems and other drainage facilities for administrative buildings, private cottages and houses, various factories, warehouses and structures. Different projects have a different purpose, level of complexity and purpose in terms of the tasks they solve.
They work both with individuals, designing the drainage of individual houses and plots, and with legal entities performing complex tasks of designing and installing discharge and drainage around shopping and business centers, warehouse complexes and factory territories.









